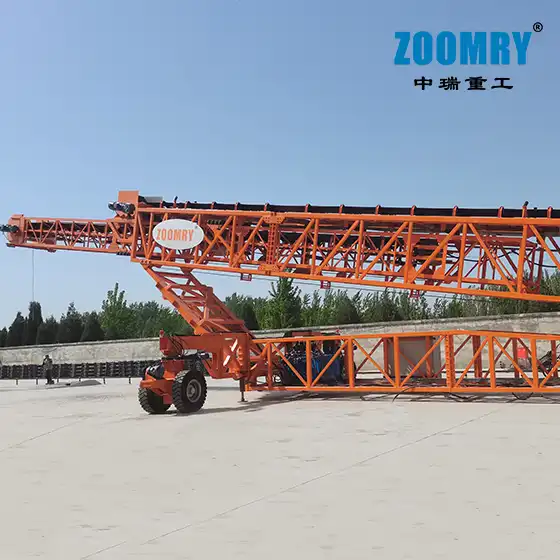
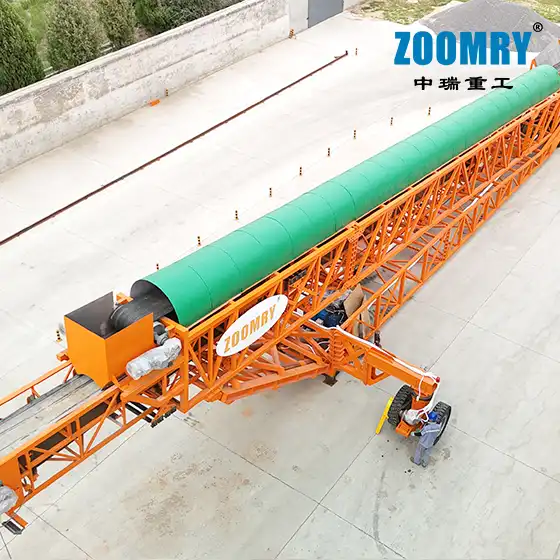
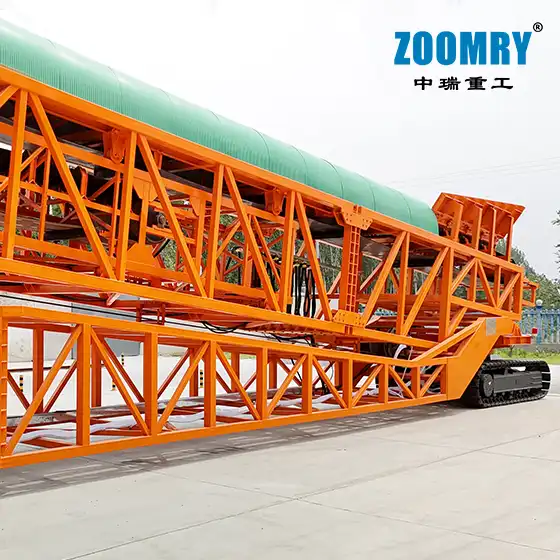
Mobile stacker conveyors are used for efficient logistics processes on construction sites. Transporting material directly from the crushing or screening plant to a dedicated stockpile means that additional material movement by wheel loaders can be avoided. This reduces operating costs and increases operational reliability and efficiency.
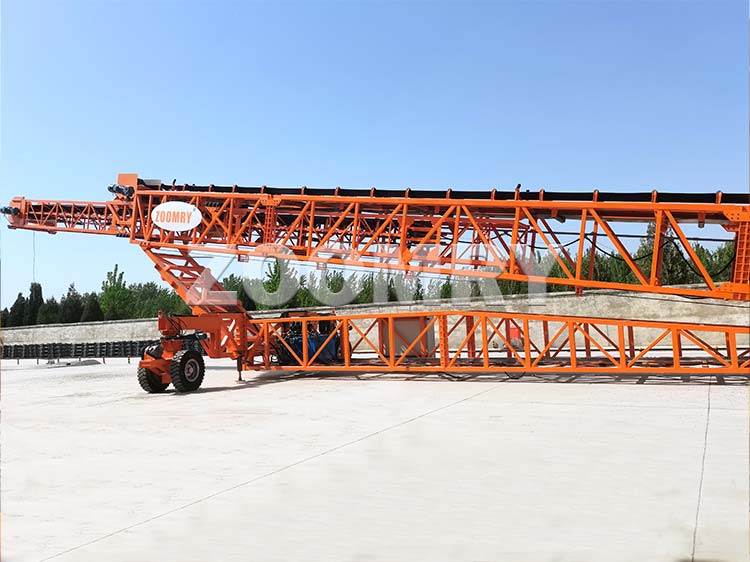

Features:
Material Transport: Our mobile stackers offer a direct and efficient material transport system from the crushing or screening plant to the dedicated stockpile. This eliminates the need for additional material movements using a wheel loader, saving you time and resources.
Customizable Configurations: We understand that each building site has unique requirements. That's why our mobile stackers are available in various customizable configurations, allowing you to adapt the equipment to your specific needs. From adjustable conveyor heights and lengths to flexible stacking capacities, you can optimize the stackers for maximum productivity.
Advanced Control System: Equipped with an intuitive control system, our mobile stackers empower operators to effortlessly manage the material transport process. With user-friendly interfaces and precise controls, you can ensure seamless operation while maintaining full control over the stacking process.
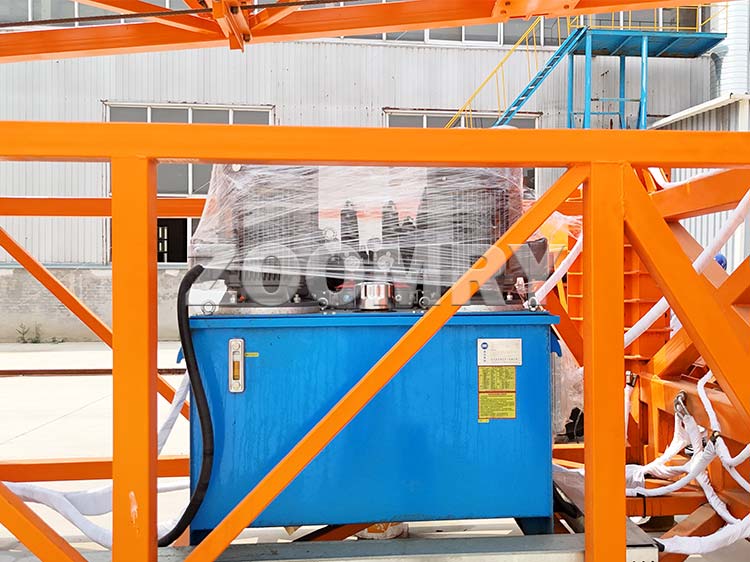

How it works
The Mobile Stacking Conveyor Tripper (MSCT) travels along the top chords of the MSC. The tripper “trips,” or transfers, material onto the cross-Conveyor Belt and discharges the material onto the stack. The cross conveyor is bi-directional and designed to advance-stack (where the MSC travels on top of the stack that it is creating) and/or retreat-stack (where the MSC travels in front of the stack that it is creating).
We have engineered the MSCT and cross conveyor to provide an adequate setback from the stack edge for advance stacking, as well as keeping the crawler track back from the advancing toe of the stack embankment during retreat stacking. In situations where the newly stacked material may have an unstable embankment, the mobile spreader is used in series with the MSC to afford an added safety factor to the setback on the advance-stack.

Specification:
| Model | Width/mm |
Maximum Capacity m3/h |
Speed m/s |
Standard length/m |
Maximum angle |
Telescopic length/m |
| ZR80SF | 800 | 500 | 2.5 | 30/40/50 | 20° | 10-20 |
| ZR100SF | 1000 | 850 | 2.5 | 30/40/50 | 20° | 10-20 |
| ZR120SF | 1200 | 1500 | 3.15 | 30/40/50 | 20° | 10-20 |
| ZR140SF | 1400 | 2100 | 3.15 | 30/40/50 | 20° | 10-20 |
| ZR160SF | 1600 | 3500 | 4 | 30/40/50 | 20° | 10-20 |
The above are our standard models, we can customize production according to customer needs.
We have a long and solid cooperation with SEW and Flnders and look forward to your inquiry.
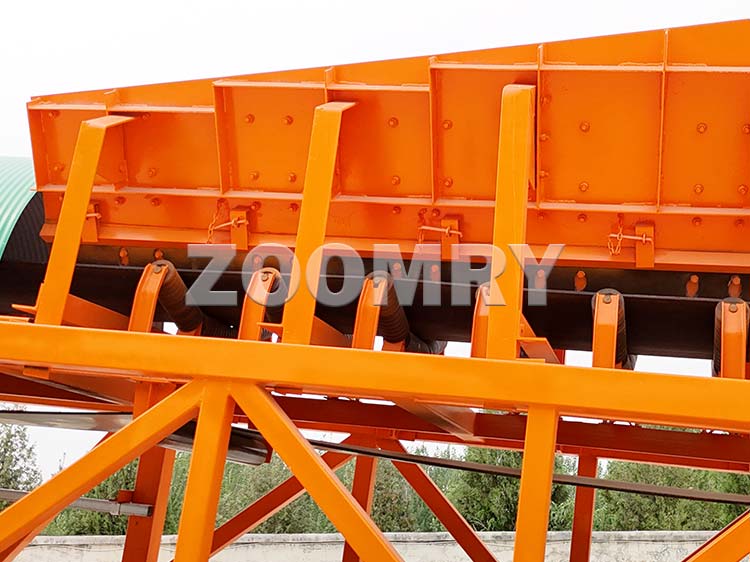

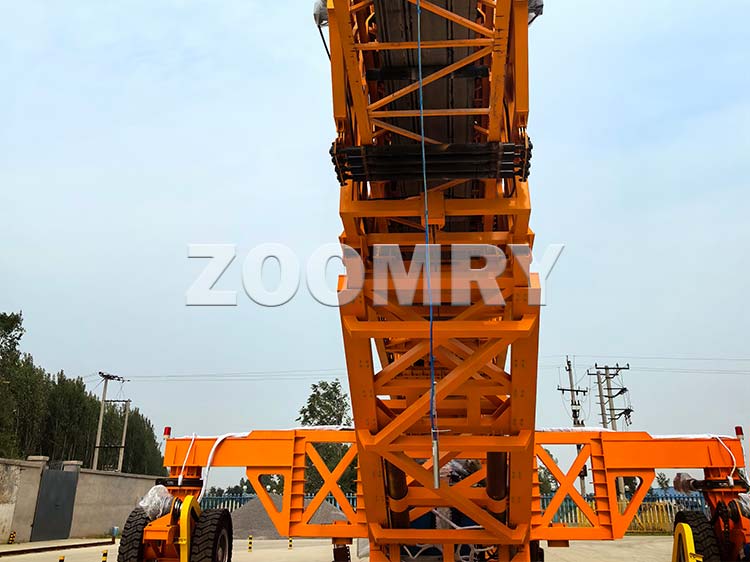
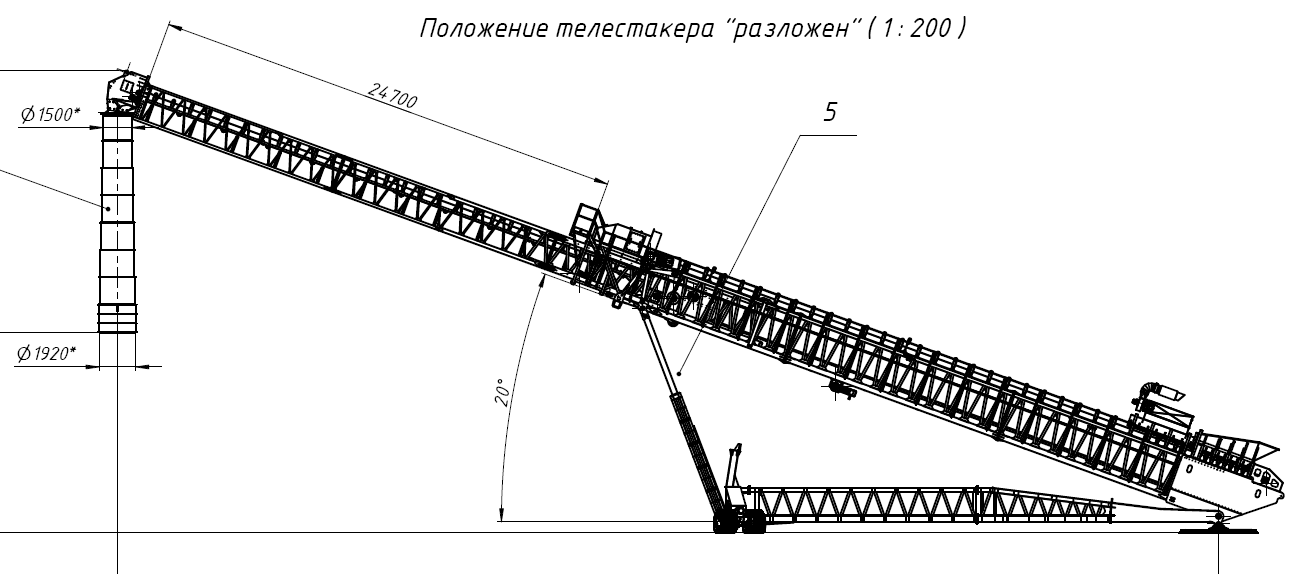
Structural composition of stacker
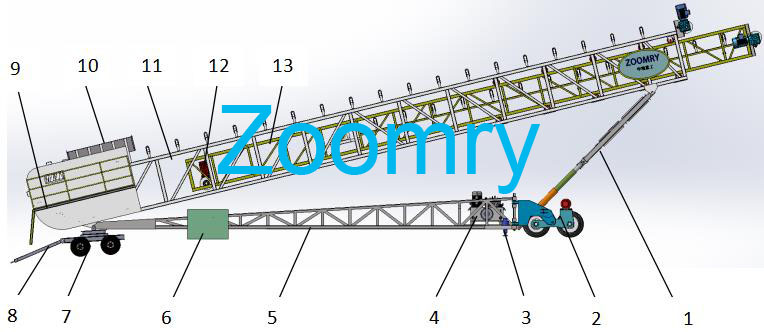
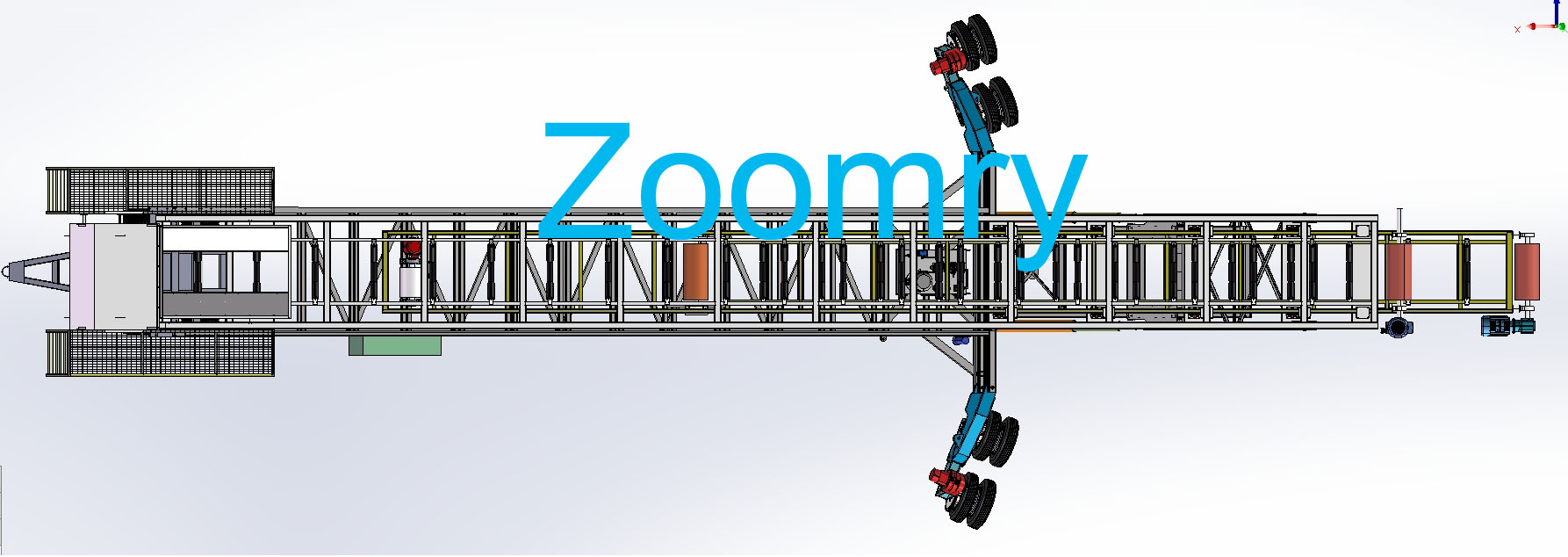
1-Hydraulic lifting system 2-Front wheel walking device 3-Hydraulic outriggers 4-Hydraulic station system 5-Base 6-Electrical control box 7-Tail wheel rotation device 8-Tow bar 9-Maintenance platform 10-Hopper 11 -Main belt conveyor 12-Wire rope traction device 13-Telescopic belt conveyor
More details:
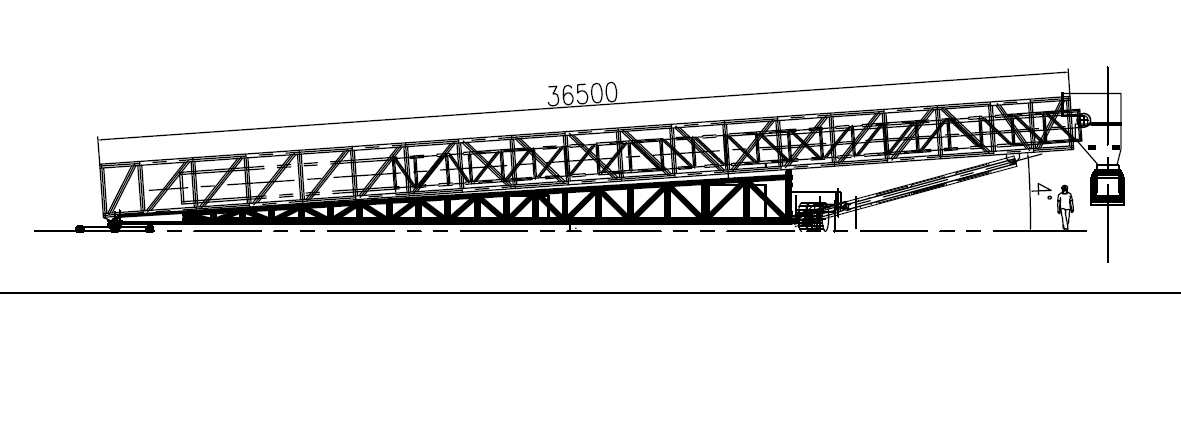
Zoomry, a leading manufacturer in the field of mobile stackers, presents an innovative solution that sets new standards in efficient material transport and logistics processes on building sites. Our mobile stackers provide unparalleled features, advantages, and applications, enabling you to streamline your operations while significantly reducing costs.
Advantages:
Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for additional material movements with a wheel loader, our mobile stackers significantly reduce operating costs. The direct transport from the plant to the stockpile minimizes fuel consumption, labor requirements, and maintenance expenses, leading to substantial cost savings over time.
Increased Operational Reliability: With Zoomry Mobile Stackers, you can rely on a robust and durable solution that enhances operational reliability. Our stackers are engineered with high-quality components, ensuring reliable performance even in demanding environments. By minimizing material handling and potential human errors, you can enhance overall site productivity.
Enhanced Efficiency: The seamless integration of our mobile stackers into your logistics processes unlocks unprecedented efficiency gains. By optimizing material transport, you can minimize downtime and maximize productivity. The precise control system allows for quick and accurate adjustments, further improving efficiency and reducing operational bottlenecks.
Application:
Zoomry Mobile Stackers find applications in a wide range of industries and projects, including but not limited to:
Construction sites: Efficiently transport materials such as aggregates, gravel, sand, and concrete from the production plant to designated stockpiles.
Mining operations: Streamline material handling in mining sites, reducing the reliance on costly and time-consuming manual labor.
Port and terminal operations: Optimize logistics processes at ports and terminals by swiftly moving bulk materials from ships to storage areas or onward transportation.
Comparisons:
When compared to traditional material transport methods, Zoomry Mobile Stackers stand out due to:
Reduced manual labor: Unlike wheel loaders or manual handling, our stackers minimize the need for manual labor, reducing physical strain and improving worker safety.
Lower operating costs: By eliminating the extra steps involved in material transport, our stackers save on fuel consumption, labor costs, and maintenance expenses.
Increased precision: The advanced control system and customizable configurations enable precise adjustments, ensuring accurate stacking and reducing material waste.
The included angle of the stacker can be controlled between 4 degrees and 20 degrees.

 ZOOMRY
ZOOMRY